Project Details
Awards & Nominations
Elite has received the following awards and nominations. Way to go!
The Challenge | Internet on the Ocean
Wi-Ocean-Max
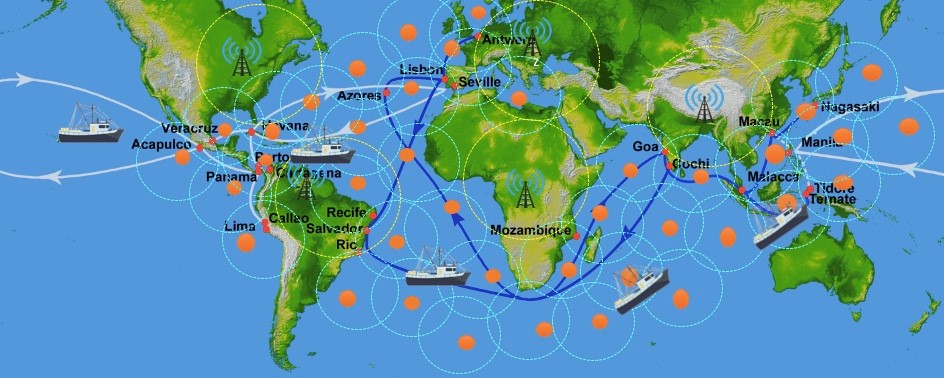
Wi-Ocean-Max is a set of devices connected to each other through a mesh network, creating a coverage area of up to 25 km of radius per device.

CHALLENGE| INTERNET ON THE OCEAN
SECCION 1: WI-OCEAN-MAX (WOM)
WOM or sea of points is a network system with a range of up to 50km of radio per device, this system has wimax signal transmitters that would be interconnected with each other and strategically located at sea through a mesh network to create a large area of coverage replacing the high cost of the satellite signal. Thus being one of the prototypes responsible for transmitting internet in the ocean.
Feature of this type of network
Higher productivity at more distant ranges (up to 50 km.)
- Better bit rate / second / Hz over long distances.
Scalable system
- Adding Easily channel adaptations: maximizes cell capacities.
- Flexible bandwidths that allow the use of licensed and license-free spectra.
Coverage
- standards-based mesh support and smart antennas.
- differentiated level services: E1 / T1 for business, better effort for domestic use.
Our mission
- Create a device that is capable of expanding and providing connection to hard-to-reach places such as the ocean or areas where there is very little coverage.
SECCION 2: Explanation
Wi-ocean-max is an initiative that originates thanks to the search for a cheaper and more accessible alternative to bring internet to the ocean. For this, a buoy system will be used that will be able to receive and expand a set of signals via WiMax.
What is WiMax?
WiMax is a communication technology similar to WiFi but by microwave with a range greater than 30km and speeds of up to 124Mbps. So far the fastest Wi-Fi networks are about 54Mbps and with a maximum coverage of about 300 meters. It is the firm candidate technology to offer super fast Internet connections and with very wide coverage.
WiMax allows you to have a connection similar to a traditional ADSL with cable, but in this case without wiring, which allows mobility between the equipment.
With WiMax there is no need for a cable connection between the subscriber's terminals and the WiMax base station and it can support hundreds, even thousands of subscribers with a single base station.
Comparison between wimax and satellite
Satellite | |
Wimax
|
Why do we use WiMax and not Wi-Fi?
The big difference with Wi-Fi and WiMax is its huge coverage distance and WiMax is much faster. But not only that, with WiMax we will have coverage even in motion, traveling at speeds of up to 250Km/h we will have coverage. Wifi is also designed for indoor environments, while WiMax is designed for outdoor environments, allowing access to more than 1000 users simultaneously.

How does WiMax work?
As the name itself explains, the base station is the place where WiMax signals are transmitted.
It consists of electronic devices and the WiMax tower or base station. This tower works exactly like the towers of network phones located at an elevated point to broadcast radio signals, but the WiMax antenna emits microwave signals.
How do we plan toimplement this set to Wi-ocean-max?
Wi-ocean-max will work through a system of transmission towers connected to each other in order to maintain and propagate a signal through a strategic scale to create a better coverage area. For the implementation of these towers we have thought and developed a systematic model of buoys that will be able to receive and expand the WiMax signal.
Each buoy will be located in several strategic points in which each one will have a distance of 20 to 30 km between them.
To locate the buoys in the sea, it is first necessary to have a service center that provides a main connection, then an outline of how it works:
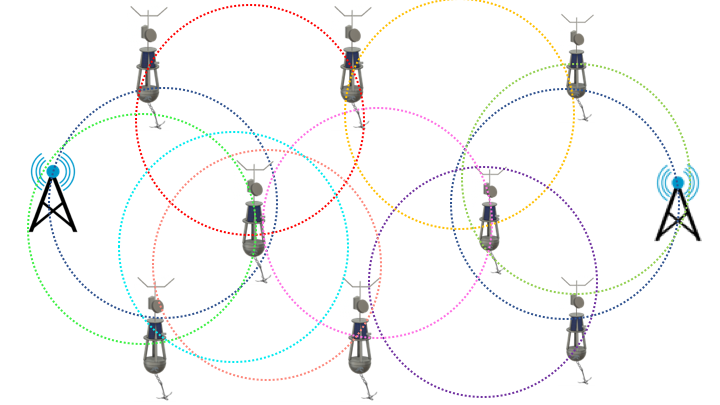
Wi-ocean-max will have a GPS system and autonomous hardware for its best performance.
Mesh network
The meshed wireless networks, coupled networks, or wireless mesh infrastructure networks, to define them in a simple way, are those networks in which the two topologies of the wireless networks, the Ad-hoc topology and the infrastructure topology are mixed. Basically they are networks with infrastructure topology but that allow devices to join the network that despite being outside the coverage range of the access points are within the coverage range of a network card (TR) that directly or indirectly is within the coverage range of an access point (PA).
They allow network cards to communicate with each other, regardless of the access point. This means that devices that act as a network card may not send their packages directly to the access point but may pass them on to other network cards to reach their destination.
For this to be possible, it is necessary to have a routing protocol that allows the transmission of information to its destination with the minimum number of hops or with a number that is not yet the minimum, is good enough. It is resistant to failures, since the fall of a single node does not imply the fall of the entire network.
The use of WiMax 5.4 GHz can be a backhaul solution, acceptable to strengthen the scope of the mesh network, but in many cases it means the renunciation of the band 5.4 GHz, to give access to users.
Using licensed technologies (for example 802.16, in the 3.5 GHz band), for the creation of the backhaul, it is possible to offer access to users in 2.4 GHz and 5.4 GHz. This allows users to have 80% more free channels , increasing the number of concurrent users by 60-80%.
As an example we can see the structure of a meshed wireless network formed by eight nodes. You can see that each node establishes communication with all other nodes.
SECCION 3: plus
GPS
You will have a Global Differential GPS (GDGPS) system that is a full-time, highly accurate and extremely robust GNSS monitoring and augmentation system.
Using a large terrestrial network of real-time reference receivers, an innovative network architecture and real-time data processing software, the GDGPS system provides time transfer accuracy below nanoseconds anywhere in the world.
Hardware
Constant of a compact, autonomous and floating type buoy unit, as well as a self-cleaning measurement management system, confirming great autonomy and minimizing maintenance operations.
The system is composed of the following elements:
Functionally
Carry out measurements continuously, enabling the configuration of data recording intervals.
The use of microprocessor technologies of very low consumption, together with an advanced control software that guarantees that the equipment can limit the energy consumption that, together with the integrated battery charging system from its generator system, extend its operation indefinitely autonomous.
It incorporates the ability to transmit information in real time or differently, thanks to the communication system between devices.
The established communication protocol is compatible with all control centers of the automatic water quality information system network.
Cleaning cycles are carried out periodically to guarantee the quality of the measurements and extend the autonomy of the system.
The data is transmitted to a control center automatically for analysis and exploitation.
Featured Features
• Ease of change of location.
• Easily transportable.
• Energy autonomy.
• Automatic cleaning system that guarantees long periods of measurements.
• GPS positioning.
Elevator
One of the biggest problems facing our buoy are the big waves that could be encountered, to avoid this we have thought of a device that works in an automated way and in a very similar way to an elevator.
This device will have an intelligent memory in which the data of the highest waves that can be generated according to the conditions of the environment will be saved, then, by means of a cylinder it will position the antenna of the buoy in such a way that the waves do not interfere with the Waves emitted by Wimax antennas.
In other words, this device will be able to extend its antenna a few meters up to avoid interference in the signal or its coverage.
Types of energy
Wi-ocean-max will be available, feeding mainly on a tidal power system, which benefits the autonomy of the devices and their performance, in addition to this, it contacts a small wind part that will be activated if there is a problem in the storage of energy or in some of the engines.


SECCION 4: Buoy design
Objective
The main objective is to validate the use of biocomposites in the manufacture of marine buoys, to avoid the negative impact on the environment when using organic materials.
The most commonly used materials for the manufacture of these marine buoys are synthetic thermoplastic polymers (polypropylene, polyethylene, etc.), that is, materials that are highly dependent on petroleum and that generate an inert solid residue after their end of life.
In this work the manufacture of a marine buoy with environmentally sustainable materials has been considered, using a resin of vegetable origin reinforced with natural fibers.
Likewise, among the different manufacturing processes of composite parts, the best option has been studied to achieve a quality product, mechanically resistant and from the operator's point of view, clean and safe.
Polymer matrix composite materials A polymer matrix composite material is formed by a component substance that acts as reinforcement, supported by another that acts as a binder material, known as matrix or resin. The combination of different resins with different materials or fiber arrangements (fiberglass, carbon, organic or polymer, among others) allows to obtain materials with very special mechanical properties that adapt to the different aspects that a certain design requires The most used thermosets for the production of laminates as matrix are polyester, epoxy and polyamides. Polyester is mainly used with glass fibers and allows applications up to 100 ° C. Epoxies are more expensive but have better moisture resistance, less dimensional variations during curing and can withstand operating temperatures up to 175 ° C. Polyamide allows applications at high temperatures, up to 300 ° C, but requires a more complicated production process.
Fibers are responsible for the structural properties of the composite. Above all, they make the composite material have high specific stiffness and resistance properties in its longitudinal direction, and also offer high energy absorption, reduce noise and vibrations, and behave better in fatigue than metallic materials such as steel or aluminum.
Materials
- Fiberglass
- Polifondo
- Catalyst: Methyl ethyl ketone peroxide
- Accelerator: Cobalt Octorate 6%.
- Red Gelcoat (Gelcoat Resichim GMV- 5005 VM RED NO AP).
- Demolishing wax
- Epoxy resin obtained from natural and renewable products.
- Advanced polyamide tubes: allow both suction and
- Injection of the resin inside.
- Spiral tube: INFUSIONWRAP 12/16 used to distribute the resin on the surface of the laminate and extract the remaining air and resin.
- "Peel ply" or peelable polyamide fabric allows
- Bag of empty
- Drainage mesh
- Adhesive joint
- Vacuum pump
- Resin trap
- Linen
 Parts of the buoy: https://github.com/anthonyalex11/SpaceApp/blob/mas...
Parts of the buoy: https://github.com/anthonyalex11/SpaceApp/blob/mas...
SECCION 5: Plans in the future
- To connect the world through a wireless network in an easy and much cheaper way than any of the methods already used in the market.
- Since creating a wide coverage area in the ocean has been a challenge until now, it has been difficult to transfer data in the systems used to monitor the climatic conditions in your environment, now thanks to Wi-ocean-max it will be easier the transfer of data since its extensive transmission system will help to obtain each one from the ocean to the ground control center.
- Create a control system (Elite) where through an app (SCE) the routes of the ships will be registered on a daily and efficient way, in order to mobilize the wi-ocean-max automatically and that thanks to this way they are rearranged in a strategic way where they can cover the area without coverage, that means, that the user when planning their trip, the application will automatically save the route and the wi-ocean-max will be deployed assuming a position that favors the Travel coverage since each device has a perimeter and all together will create a coverage mesh where it will be difficult for the connection to be lost or weakened in such a way.
SECCION 6: RESOURCES
https://core.ac.uk/download/pdf/13283470.pdf
https://www.prensa.com/cultura/Wimax-arremete_0_1861314023.html
http://www.puertos.es/es-es/conceptosgenerales/Paginas/Sistema-GPSDGPS.aspx
http://rutasblog.blogspot.com/
http://recursostic.educacion.es/secundaria/edad/4esofisicaquimica/4quincena11/4q11_contenidos_2d.htm
https://commotionwireless.net/es/docs/cck/networking/guidelines-for-mesh/
https://es.wikipedia.org/wiki/Red_inal%C3%A1mbrica_mallada
https://www.dhn.mil.pe/Archivos/Oceanografia/normastecnicas/NormasTecnicasHidrograficasN%C2%B023.pdfTool used
- Autodesk fusion 360
- Afer effect
- Imovie