Project Details
The Challenge | Internet on the Ocean
sh_Ip
Sh_IP proposes the construction of an Internet network consisting of 1000-4000 ships carrying network equipment (reception / distribution / signal multiplication), which travels daily on the New York - Southampton commercial shipping route.
Our solution offers cheaper internet access, higher speeds at over 1250 miles from shore, by a data packet on each ship and eliminating satellite communication ($ 4/1 Mb) and satellite communication antenna.
I. General informations about the route
Route type:commercial, for ships 100 - 200 metric tons
Length : 3110 nautical miles = 5760 km = 3579 miles
Denstity transportation /day
Number of ships on the route : 4 000 at any moment
1 line
3110 miles/2 miles safety distance between ships = 1555 ships/day
4 000/1 555 ships/route = 3 lines
duration 8-10 days
salinity on route (see photo)
very high https://bit.ly/32x6Hyy
Climate Air currents are mosty from west to east http://www.scritub.com/files/geografie/775_poze/image004.jpg
stormsfrequency storms - 10 - 16/year (hurricanes 4-8 /day)
period June - December
power level 2 - 4 https://www.nhc.noaa.gov/aboutsshws.php?fbclid=IwA...
II.Internet Services Information’s today:
- Internet services are available only on a limited number of ships, whether they are cargo or cruise or military; internet speed has reasonable values only about 1250 miles off shore. After crossing this limit, the speed and bandwidth have low values.
- VSAT Equipments on board are very expensive: from 5000-50000$;
- About 4$ per megabytes;
- Mobile Dial-up has very weak signal;
III.Challenges:
High Speed Wind, high waves, storms have been factors that deny us the possibility of deploying equipments in the air or on the surface of water.
Because of this impediment we put all equipment’s on ships and we create amore efficient network architecture.
Power supply for equipment is another big issue because you cannot generate a high amount of energy on board and solar power isn’t a feasible source because of the salinity of water, high risk of damaging because of the waves.
Maintaining the equipment deployed on the surface of the water would have been very hard and challenging to reach every equipment in the middle of the ocean so we avoided this solution.
Technical details:
A ship is going offshore for about 8 miles. The probability of this to happen is 0%;
Is the ships are going more than this 8 miles value the network is still working because of the redundant protocol.
The issue about this topology is about overloading an equipment. To avoid this we use DTN
We would use a watchdog timer to avoid overcharging the CPU.
IV.Technical presentation of the solution
Please see attachement.
V.Buget
Please see attachement.
VI. Project implementation strategy
S1: Create configuration along the route
S2: Construction of data packages for ships
S3: Implementation of the coastal network infrastructure (port)
S4: Sale of packages to shipping companies
S5: Installation and configuration
S6: Maintenance
VII. Duration
Regarding the time required to implement the topology forabout 1000 ships we estimated a duration of 3 years
VIII. Risks
We won’t be able to manage to implement the solution on enough ships (min. 1000 ships)
- we do not find rental space for shore equipment, in ports
-we can't find an internet provider on the shore
Technical description:
Taking into consideration the cost and complexity of implementation, we’ve opted against using ViaSatellite services: a ViaSatellite link can achieve speeds up to 432kbps at a maximum monthly cost of $20 000, given daily usage
The proposed network topology is WMN (Wireless Mesh Network). In summary, such a network is composed of a large number of radio interconnected Access Points, using different technologies (WiMax 802.16 has been chosen for this project). Each part of the network (mesh router installed onboard the naval ship) can be either a gateway or a repeater to the close node in its proximity.
Within a WMN network, the equipment can fulfil the following roles: client, router, gateway.
Benefits:
• decrease in the number of gateways;
• increased redundancy;
• Dynamic IP and routing configuration;
• Reliable;
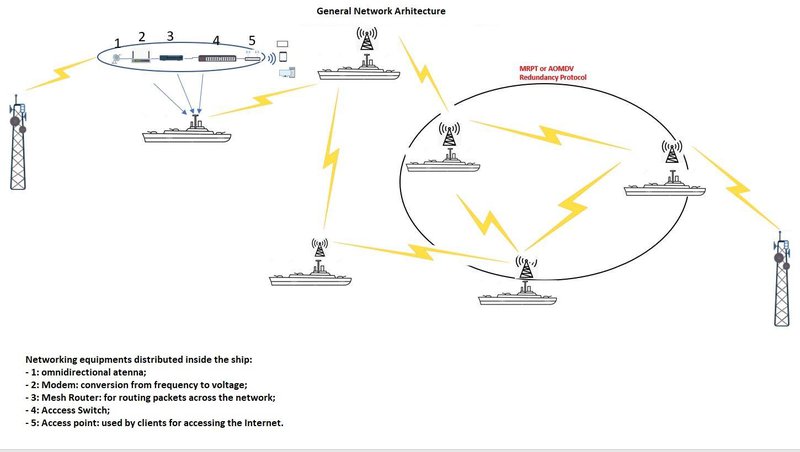
The proposed network architecture consists of:
BS (Base Station) arranged along the shores at a considerable distance from each other, so as not to interfere with each other. They have the role of being the "provider" of Internet services. They are connected to local ISP (Internet Service Providers) through high-speed optic fiber links (10gbps). Important aspects regarding the installation of the BSs: The height of these, preferably 40-50 meters to have a LOS (Line of Sight) as good as possible. The BS transmits using radio technologies called WiMax or VHF (Very High Frequency) modulated radio signal representing " Internet services”. The recommended power is ordinarily at the level of hundreds of watts in order to reach the maximum transmission distance with high signal quality, but without causing station damage (over-heating).
WiMax features which are important for this proposed architecture:
• The maximum distance at which this signal can reach with a reasonable quality is approximately 50km according to IEEE 802.16 standard. This distance can obviously be modified depending on the atmospheric conditions.
• Maximum speed reached: 70mbps (usually); Implementing the latest variant of WiMax rel 2.0 can reach 365 mbps using two broadcast channels and two receivers in a 20MHz band MIMO (Multiple input multiple output) architecture.
• No Line of Sight required. Perhaps the most important aspect of the chosen technology is the lack of direct visibility between the BS and the antenna placed on the ship. Atmospheric reflections and reflections on the sea surface are useful aspects in the maritime environment for radio communications.
Omnidirectional reception antennas: their role is to retrieve the signal from the BSs or from the equipment in their vicinity, which will serve as a service provider.
Mesh routers: Mesh-type equipment that supports routing protocols specific to WMN architecture, gigabitethernet traffic capabilities, qos functions and other traffic control specific functions.
For a better redundancy, two pieces of equipment can be installed per ship, one with active role and one called cold reserve, in case of irreparable failure of the main equipment.
Access switches: The only requirement is to have gigabithethernet ports and support for loop free service.
Access Point: Role of user interface with the network. This number is proportional to the size of the ship and the number of people on board who are entitled to internet services.
The only challenges in choosing the types of equipment are related to the antenna: this one has to support transmission and reception in the appropriate ranges, the distance to which it can send and from which it can receive signal.
The network equipment itself can be chosen according to the budget available during the implementation of the final solution.
The biggest challenge regarding the network’s architecture is providing redundancy and 100% network uptime. There are currently around 70 routing protocols for WMN networks. For this implementation MRPT (MAC-based Routing Protocol for Triton) or AOMDV can be chosen. MRTP would be the preferred choice because of the proactive capabilities, multi-path traffic, higher throughput and lower delay as compared to the earlier mentioned options. In order to improve the network's rate of transfer and reduce the latency caused by data loss, we'll integrate the Disruption Tolerant Networking protocol at the router's software level (as a network driver) and use an external RAM drive connected to the router via USB 3.0 to store the network traffic that's waiting to be sent.Taking into consideration the cost and complexity of implementation, we’ve opted agains using ViaSatellite services: a ViaSatellite link can achieve speeds up to 432kbps at a maximum monthly cost of $20 000, given daily usage
The proposed network topology is WMN (Wireless Mesh Network). In summary, such a network is composed of a large number of radio interconnected Access Points, using different technologies (WiMax 802.16 has been chosen for this project). Each part of the network (mesh router installed onboard the naval ship) can be either a gateway or a repeater to the close node in its proximity.
Within a WMN network, the equipment can fulfil the following roles: client, router, gateway.
Benefits:
• decrease in the number of gateways;
• increased redundancy;
• Dynamic IP and routing configuration;
• Reliable;
The proposed network architecture consists of:
BS (Base Station) arranged along the shores at a considerable distance from each other, so as not to interfere with each other. They have the role of being the "provider" of Internet services. They are connected to local ISP (Internet Service Providers) through high-speed optic fiber links (10gbps). Important aspects regarding the installation of the BSs: The height of these, preferably 40-50 meters to have a LOS (Line of Sight) as good as possible. The BS transmits using radio technologies called WiMax or VHF (Very High Frequency) modulated radio signal representing " Internet services”. The recommended power is ordinarily at the level of hundreds of watts in order to reach the maximum transmission distance with high signal quality, but without causing station damage (over-heating).
WiMax features which are important for this proposed architecture:
• The maximum distance at which this signal can reach with a reasonable quality is approximately 50km according to IEEE 802.16 standard. This distance can obviously be modified depending on the atmospheric conditions.
• Maximum speed reached: 70mbps (usually); Implementing the latest variant of WiMax rel 2.0 can reach 365 mbps using two broadcast channels and two receivers in a 20MHz band MIMO (Multiple input multiple output) architecture.
• No Line of Sight required. Perhaps the most important aspect of the chosen technology is the lack of direct visibility between the BS and the antenna placed on the ship. Atmospheric reflections and reflections on the sea surface are useful aspects in the maritime environment for radio communications.
Omnidirectional reception antennas: their role is to retrieve the signal from the BSs or from the equipment in their vicinity, which will serve as a service provider.
Mesh routers: Mesh-type equipment that supports routing protocols specific to WMN architecture, gigabitethernet traffic capabilities, qos functions and other traffic control specific functions.
For a better redundancy, two pieces of equipment can be installed per ship, one with active role and one called cold reserve, in case of irreparable failure of the main equipment.
Access switches: The only requirement is to have gigabithethernet ports and support for loop free service.
Access Point: Role of user interface with the network. This number is proportional to the size of the ship and the number of people on board who are entitled to internet services.
The only challenges in choosing the types of equipment are related to the antenna: this one has to support transmission and reception in the appropriate ranges, the distance to which it can send and from which it can receive signal.
The network equipment itself can be chosen according to the budget available during the implementation of the final solution.
The biggest challenge regarding the network’s architecture is providing redundancy and 100% network uptime. There are currently around 70 routing protocols for WMN networks. For this implementation MRPT (MAC-based Routing Protocol for Triton) or AOMDV can be chosen. MRTP would be the preferred choice because of the proactive capabilities, multi-path traffic, higher throughput and lower delay as compared to the earlier mentioned options. In order to improve the network's rate of transfer and reduce the latency caused by data loss, we'll integrate the Disruption Tolerant Networking protocol at the router's software level (as a network driver) and use an external RAM drive connected to the router via USB 3.0 to store the network traffic that's waiting to be sent.