DMD - ДМД| Rise to Resilience!
Project Details
The Challenge | Rise to Resilience!
Water management system
Green infrastucture for urban areas. Sustainable way of water management in cities :: https://drive.google.com/open?id=1gOVylhlc7j3cEjYn5SjhE8l-yLM22_m2
Roof gardens
The roof garden is the core point of this project. The roof garden is basically a self-sustaining garden constructed on the roof of a building with plants such as dwarf fruit trees, plants that generate a larger amount of oxygen per space taken up and which are local. The plants are planted in a manner such that their needed amount of water is less than the gathered water from rainfall in the garden area. The plants help us with reducing the carbon dioxide in the air, increasing the humidity of the air, refine the rain water and are part of a system that both makes a use of the rain water and reduces the risk and intensity of a potential flood. The plant’s fruits will be used to fertilize the soil and the surplus is collected by the residents of the building.The plants food could also be used for eating and soil could be fertilized manually. Also, some other additional gardening work may be required, thus creating new jobs for agronomy.
Soil
The soil will be constructed so that the dirt is going to be on top and it is where the plants will be planted, below that there will be layers of rocks from smaller to bigger so the water would move slowly downward where the rocks will be met with a metal net and a funnel where the water is going to be extracted and sent down to the reservoir.
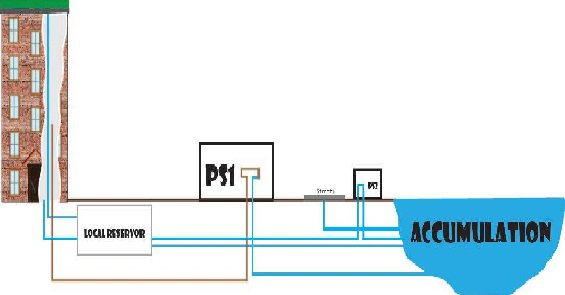
The reservoir
The reservoir is a container constructed at the lowest site of the building with a volume that is calculated by using information such as building size, rooftop area and annual precipitation. The reservoir’s water is later filtered using chlorine and used in watering the plants (If the soil of the garden lacks a certain mineral it will be added to this water) and assisting the water management for the toilets, thus providing an economical benefit from the whole project. The surplus of water is invested in a creation of an artificial accumulation.

Water filtering station
The water from the reservoir before going to its designated location goes through the water filtering station in which the water is filtered using chlorine and carbon filters. The water that is planned for watering the plants goes only through a chlorine-based filter so It eliminates the microbes from the water, but doesn’t remove the minerals from the water that the plants might later use. The rest of thereservoir water both through a chlorine and carbon filter to prevent forming cyanides in the accumulation and for a better hygiene of the sewage and for the toilet water. If there is need for additional water, the filter station is connected to the sewage system and the sewage water can be filtered to an acceptable state using both biological and physical filtering.

The sewage
The sewage system is also a supporting asset in our concept. Sewage water is filtered whenever there is a need for additional water. The sewage water goes through a similar purification as the accumulation water and becomes part of the entirety of the system.
Accumulation
In the urban and suburban zones the extra water collected after filtration, is delivered to a basin forming an artificial accumulation. The accumulations formed are going to be settled with different animals, fish and plants to form a mini ecosystem. The accumulations are a great ecological asset to the cities. They hold part of the water from potential floods, thus reducing the likelihood and damage of a flood. accumulations also present a surface from which water would evaporate and an opportunity for green life to flourish. The accumulation is connected to support the roof garden if needed.