Regolith Boys| Dust Yourself Off
Team Updates

UV scanning
This file contains hidden or bidirectional Unicode text that may be interpreted or compiled differently than what appears below. To review, open the file in an editor that reveals hidden Unicode characters. Learn more about bidirectional Unicode characters
| #include<LiquidCrystal.h> | |
| LiquidCrystal lcd(12, 11, 5, 4, 3, 2); | |
| //Hardware pin definitions | |
| int UVOUT = A0; //Output from the sensor | |
| int REF_3V3 = A1; //3.3V power on the Arduino board | |
| //https://www.how2electronics.com/uv-sensor-ml8511-arduino-for-uv-ray-intensity-measurement/ | |
| voidsetup() | |
| { | |
| Serial.begin(9600); | |
| lcd.begin(16, 2); | |
| pinMode(UVOUT, INPUT); | |
| pinMode(REF_3V3, INPUT); | |
| Serial.println("ML8511 example"); | |
| } | |
| voidloop() | |
| { | |
| int uvLevel = averageAnalogRead(UVOUT); | |
| int refLevel = averageAnalogRead(REF_3V3); | |
| //Use the 3.3V power pin as a reference to get a very accurate output value from sensor | |
| float outputVoltage = 3.3 / refLevel * uvLevel; | |
| float uvIntensity = mapfloat(outputVoltage, 0.99, 2.8, 0.0, 15.0); //Convert the voltage to a UV intensity level | |
| Serial.print("output: "); | |
| Serial.print(refLevel); | |
| Serial.print("ML8511 output: "); | |
| Serial.print(uvLevel); | |
| Serial.print(" / ML8511 voltage: "); | |
| Serial.print(outputVoltage); | |
| Serial.print(" / UV Intensity (mW/cm^2): "); | |
| Serial.print(uvIntensity); | |
| lcd.clear(); | |
| lcd.print("UV Ray Intensity"); | |
| lcd.setCursor(0, 1); | |
| lcd.print(uvIntensity); | |
| lcd.print(" mW/cm^2"); | |
| Serial.println(); | |
| delay(200); | |
| } | |
| //Takes an average of readings on a given pin | |
| //Returns the average | |
| intaverageAnalogRead(int pinToRead) | |
| { | |
| byte numberOfReadings = 8; | |
| unsignedint runningValue = 0; | |
| for(int x = 0 ; x < numberOfReadings ; x++) | |
| runningValue += analogRead(pinToRead); | |
| runningValue /= numberOfReadings; | |
| return(runningValue); | |
| } | |
| floatmapfloat(float x, float in_min, float in_max, float out_min, float out_max) | |
| { | |
| return (x - in_min) * (out_max - out_min) / (in_max - in_min) + out_min; | |
| } |
C
Chrystian Portella da Silva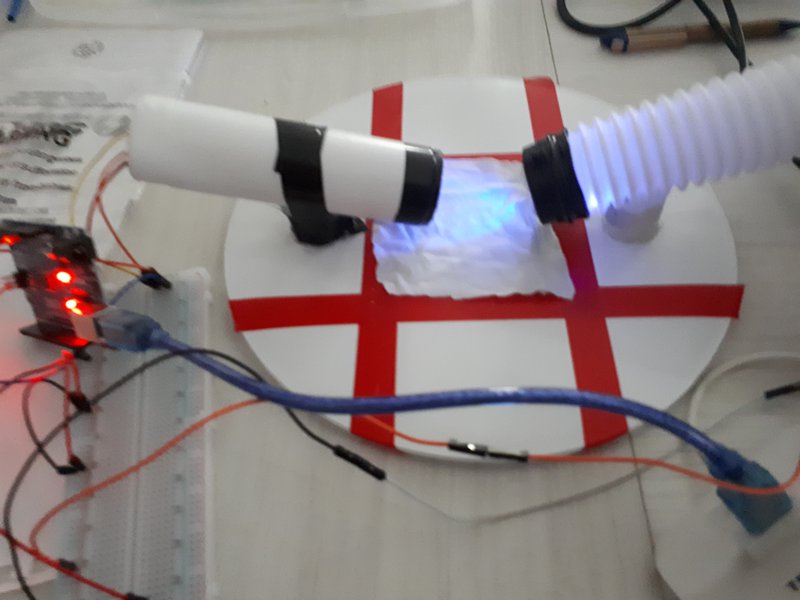
UV detecting

Remotion of dust with magnetic device
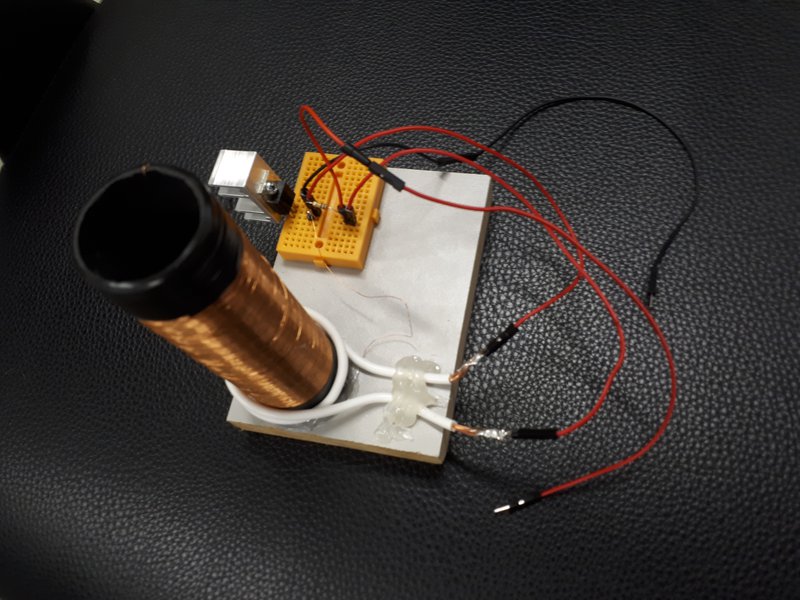
Ionization device (Tesla coin)
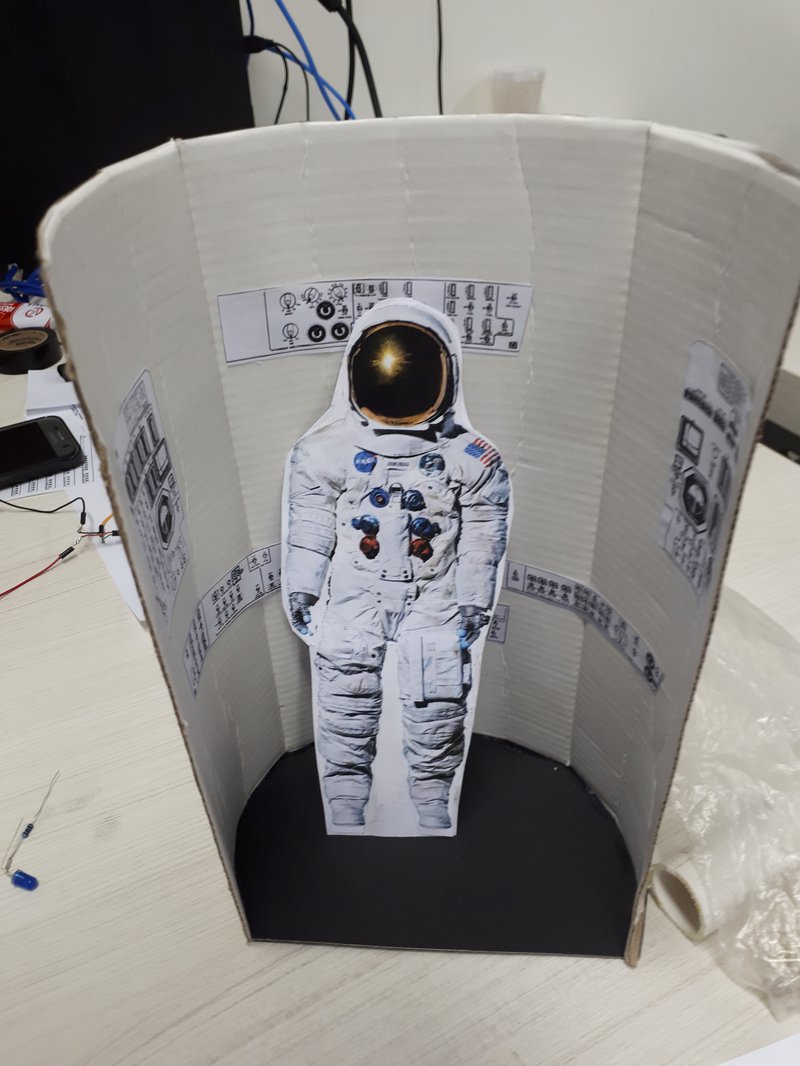

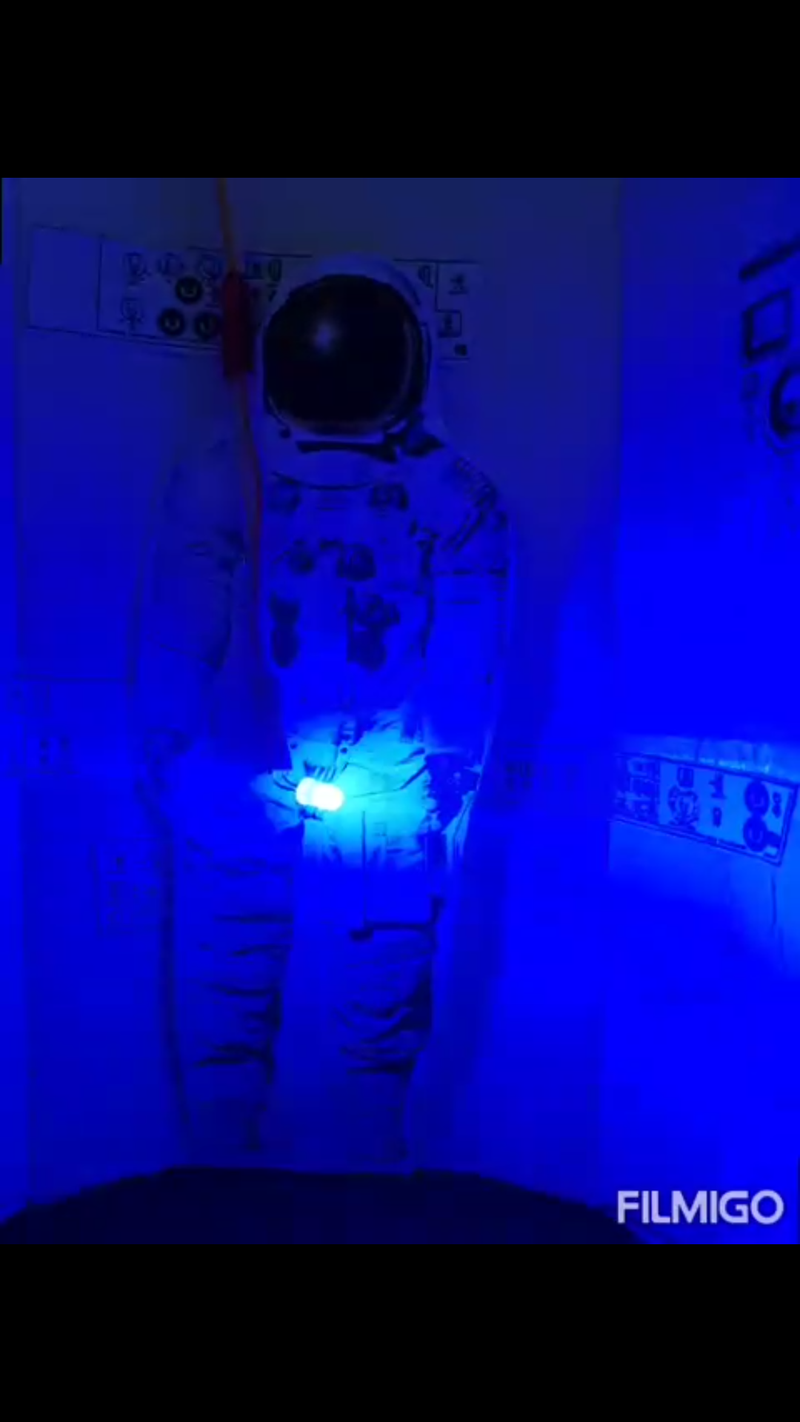
Dust Detection in Airlock Module
NASA Checklist Airlock Procedures
1 Close the Hatch.
2 Position of Astronautin Rightangle ofdetection.
3 Turn offall lights.
4 UV sensor Scansspacesuit top to downin 360 degrees to detectUV anomaly generated by regolith.
5 When sample was detectedmark the position of regolith.
6 He Ionization of local were dust was detected .
7 After Ionization uses magnets to remove the dust.
Points ofmore Ti contamination in Apollo 17 LMP Spacesuit in units of ppm X 102
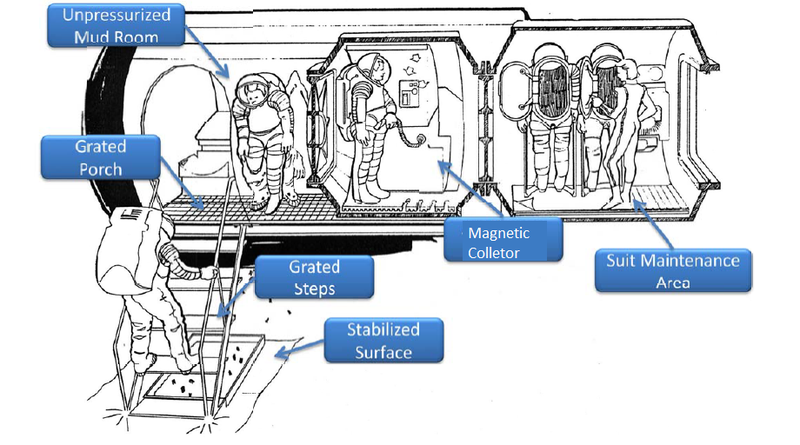
Air Lock with solution