Influencers| Trash Cleanup
Project Details
The Challenge | Trash Cleanup
Sustainable Offshore Autonomous Modular Fleet (SOAMF)
Sustainable Offshore Autonomous Modular Fleet (SOAMF) aims to collect marine debris across the ocean with no reliance on fossil fuels.
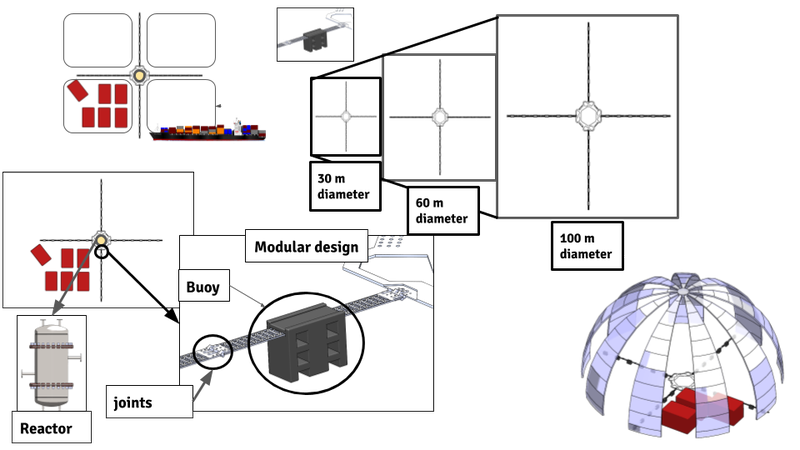
Sustainable Offshore Autonomous Modular Fleet (SOAMF)
Abstract: Marine ecosystems have long been damaged significantly by marine debris. Harming marine life, posing a threat to humans and interfering with navigation systems are several deleterious effects of intentional or unintentional disposal of garbage into the oceans. Due to the ocean currents, these piles of garbage are driven and accumulated in one place to result in patches that cover a vast area of ocean surface. The marine debris contains plastic bags, bottles, aluminum cans as well as the remnants of crashed vessels and aircrafts.
This conceptual design aims to collect ocean garbage. By utilization of approximately 100 autonomous fleets, the significant proportion of marine debris can be gathered. The designed system has a main compartment and four steel trusses attached to it. The fleet deploys mini swarm robots in order to collect the garbage nearby. Subsequently, the robots return to dock at the trusses and the collected trash is carried to the molten substance by using a specific chemical compound, which is another feature that makes this mission worthwhile. The molten substance can later be solidified and used to produce plastic materials. It is worthy to note also that the fleet is powered by means of solar panels, completely eliminating reliance on fossil fuels.
Design: Since the garbage patches are located in remote distances from landmasses, using manpower makes this particular task very arduous. The designed autonomous fleet achieves propulsion with electric motors and is capable to move in two directions and rotate around its axis. By using NASA’s Earth data, the exact locations of the accumulated debris can be found and the corresponding coordinates can be transmitted to the fleet to allow it to reach its destination. In necessary situations, a ship approaches to the fleet to replace the waste container inside the main compartment and replenish the chemical compound that is required to melt plastics. Solar panels are installed onto the main compartment and provide energy to run the electric motors.Swarm robots are charged while they dock at the trusses of the fleet. All these unique features reduce time and energy required for debris collecting operation.
The Chemistry Side: Nowadays one of the major problems that our world deals are exponentially increasing marine debris amount. To tackle it, a compound called 1,2-dichloroethane will be utilized. This is the chemical that melts, or in other words, breaks the polymer chains to make them soluble and eco-friendly for our Earth. The process is going to take part in a device that is made by two of the teammates. Basically, a compression process is going to take part which will first, provide us more space in the device which in turn would allow more plastic intake, and act as a catalyst. During the compression, the plastics which are in our case polyethylene is going to react with 1,2-dichloroethane and decompose. To be more elaborate, the chains are going to be broken by this chemical and reach to a solid phase. In the future, when 1,2 Dichloroethane is reacted with polyethylene, a glue can be formed which will be highly corrosion, water, and acid resistant. However, the process would not end here but make this output a useful and efficient material as the product of this reaction is going to be again a newly formed polymer that will be fully qualified to be used again without any processing except molding it into shape. The efficiency of this process is calculated to be nearly 95% to 98% theoretically. The eventual product of the chemical reaction is a sticky substance that can be utilized as glue in everyday life. This product may be considered a potential invention, but it needs further study and analysis.
Cost: SOAMF project offers an efficient mission in terms of cost as well. Utilization of solar panels makes appreciable reductions to energy related costs. Moreover, there is no need for continuous manufacturing of fleets, because they can be produced once in certain numbers and can be easily repaired when necessary, until the operation comes to an end after fleets clean all of the patches.
Potential problems: Although the system is designed to operate under normal conditions, it may fail under very harsh conditions. Naturally occurring phenomena such as very strong waves, storms and lightning strikes may have devastating effects for the fleet. Trusses may be overbent or subjected to twisting or torsional forces, resulting in a catastrophic failure of the system. If a more durable fleet is desired, this rough conceptual design should be examined and developed further in order to produce a solid product.
Resources:
- Clean Up Windsor Campaign Blog. (2010). Retrieved from https://cleanupwindsorcampaign.wordpress.com/tag/oceans/
- Shirah, G., & Mitchell, H. (2015). Garbage Patch Visualization Experiment. Retrieved from https://svs.gsfc.nasa.gov/4174