Project Details
The Challenge | Eeny, Meeny, Miney, Sample!
LOCUS
Lunar surface exploring rover design
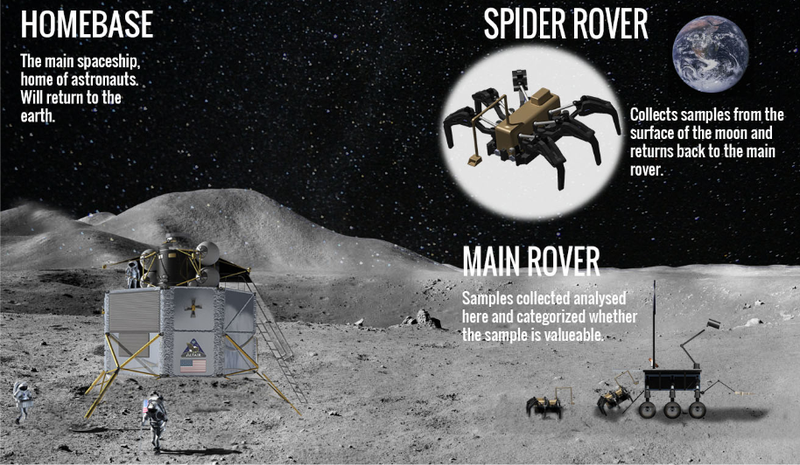
Mission Summary
We still don't know for sure how the moon came about. Scientists have done many studies before and tried to get information about the Moon. The aims of these researches are as follows:
- Seek water
- Examining rock fragments
- Examine the formation process of the moon
- Examine the inner and outer structure of the moon surface
These studies have reached today's technology. However, one of the problems we encounter when examining the structure of the Moon is that unnecessarily large amounts of time spent searching for rocks and water by astronauts.
Problem Solution
We need to get components of water from the moon and find out the isotope ratio by the rover tools. Is the Earth’s isotope ratio the same as that of the Moon? For this purpose, our rover vehicles will analyze the isotope ratio in the water by examining the ice mass waters on the moon. In this way, we will learn whether the Moon really came from outside the world, or created from the fragments of Earth.
At the same time, the samples obtained by means of the analysis devices on the Main Rover will be examined. In this way, time losses of astronauts will be prevented.
In addition, the small area will be scanned and examined optimally due to the multiple Spider Rovers. These autonomous rovers (Main Rover, Spider Rovers) will bring the best sample rock, dust examples to the astronauts. As a result, the minimum time will be spent on the searching of the best / useful rocks soils, and possible water isotypes by astronauts.
System Concept of Operations
Processes
- Main Rover will go the best possible location on the Moon autonomously.
- Main Rover will departure two Spider Rovers into the area.
- Main Rover will open the folded solar panels and wait for the spider rovers to come back.
- Spider Rovers will disperse to the area for searching for rocks and water isotypes.
- Any found rock sample will be grabbed and put into the Spider Rover’s sample baggage by the robotic arm on Spider Rover.
- Spider Rover will directly return this obtained sample to the Main Rover, where it will be re-charged.
- Main Rover will examine, analyze this sample and decide whether this sample of rock is beneficial to continue further investigation on that sample found place.
- If this speciment is valuable, the Main Rover will store this sample and the location where it is found by the Spider Rover.
- When time arrives, the Main Rover will bring the valuable samples to the astronauts.
- As a result, the efficiency of the from Moon to Earth samples will be increased.
Components
- UHF Antenna
- Supercam Camera
- Cold Gas Thrust
- Spider Movement System
- Reflector Antenna
- XRF, SEM, NDE, Spectrometers,
- Sample Baggage
- Robotic Arm
- Solar Panels
- Robotic Excavation Arm
- Sample Indoor
- Wheels
Analysis of the Samples
The Main Rover includes the following analysis tools :
- XRF (X-ray Fluorescence) : measures chemical and mineral structure of the samples.
- SEM (Scanning Electron Microscopy) : produces images with been of electrons.
- NDE (Nondestructive Evaluation) : locates a defect measures about that defect size, shape and orientation.
- Mass Spectrometer : mass of the samples can be measured with ion from chemical substances.
- Neutron Spectrometer : adequately discriminates between neutrons and charged particles and measure equivalent doses to the human body .
- Thermal Emission Spectrometer : measures the thermal infrared energy (heat) emitted from planets, tells about that planets the geology and atmosphere.
Conclusion
- As a result of these processes, the crucial astronaut time will be saved.
- Due to the multiple analysis tools on Main Rover, rocks, rock fragments, dust, core samples, and water isotypes can be analyzed.
- As a result the Main Rover being connected to the Deep Space Web, the live telemetry data will always be received on the Earth’s stations.
- Structure of the Spider Rovers’ spider movement system will allow them to climb and descent from possible steep sides of the Lunar surface.
References
- https://ntrs.nasa.gov/archive/nasa/casi.ntrs.nasa....
- https://mars.nasa.gov/mars2020/mission/instruments...
- https://www.nasa.gov/centers/johnson/partnerships/erc/mras/scanning-electron-microscopy-sem
- https://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/station/research/news/fast_neutron-spectrometer
- https://2019.spaceappschallenge.org/challenges/our-moon/eeny-meeny-miney-sample/details
- https://www.lpi.usra.edu/publications/books/lunar_sourcebook/pdf/LunarSourceBook.pdf
- https://www.lpi.usra.edu/decadal/leag/DavidJLoftus.pdf
- https://sservi.nasa.gov/
- https://www.nasa.gov/what-is-artemis